Dr. Matthew Tipper, Business Director, Nonwovens Innovation & Research Institute Limited (NIRI), UK09.12.18
To be considered flushable, wet wipes need to be compatible with disposal in wastewater systems. This is considered to include wipes not only clearing the toilet and immediate drain pipes but also passing wastewater conveyance systems and being processed in wastewater treatment systems so that they are unrecognizable in the final effluent.
The fourth edition of the INDA/EDANA guidelines (GD4), published in May 2018, details a technical protocol for assessing the flushability of wipes, as well as a label code of practice. To comply with the flushability test protocols, the composition of wet wipes should be carefully considered. The fibers that make up the wipe substrate will have a direct influence on the biodegradation performance, both aerobic and anaerobic as well as the buoyancy (settling) and toilet and drain-line clearance performance.
Disintegration (dispersibility) is a key property of flushable wipes. The ability of a wipe to break up helps to:
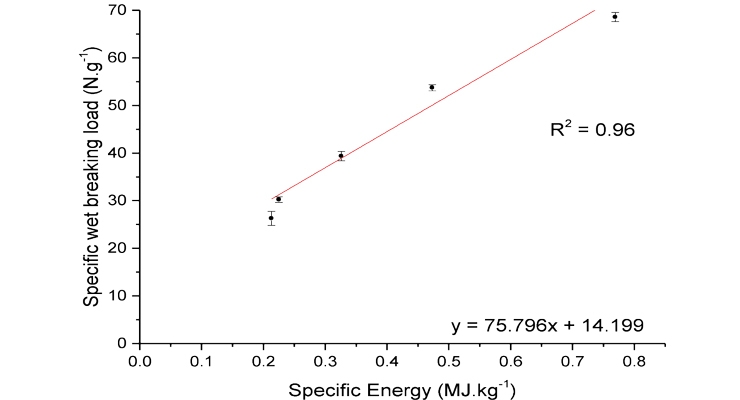
Traditional routes of producing nonwoven wipes, such as carding-hydroentanglement and airlaid-chemical bonding have not proved optimal for producing dispersible substrates, which has led to wetlaid-hydroentanglement platforms being preferred. Cellulose fibers (both wood pulp and regenerated cellulose) are wet-formed and then entangled together using high-pressure water jets to mechanically entangle the fibers together and produce the dispersible wipe substrate. The energy imparted by the water jets is important in increasing the strength with higher inputted energy leading to higher strength but also reduced dispersibility. A relatively linear relationship between hydroentanglement energy, wet strength and dispersibility is shown in figure 1.
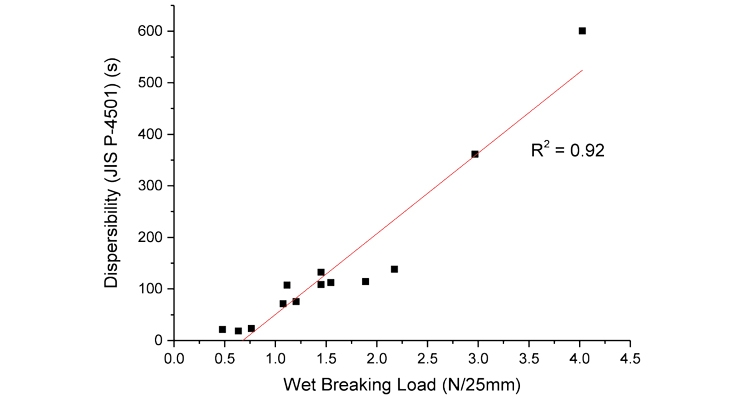
It is possible, however, to observe much higher variation in dispersibility when the wet breaking strength is above 4 N/25mm, suggesting that factors other than strength influence dispersion performance. So what are the causes of this variation in dispersibility?
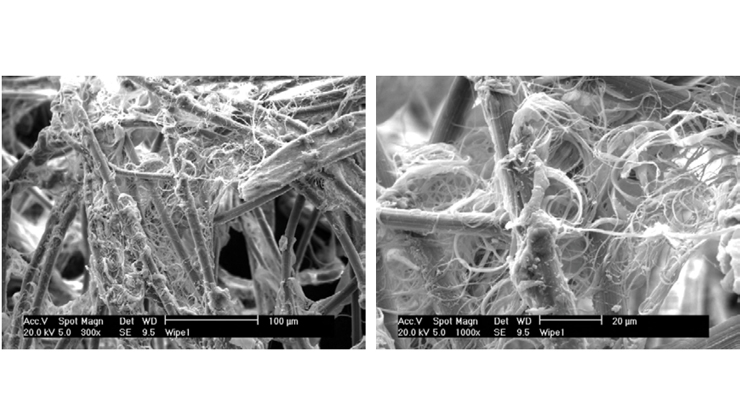
Flushable wipes are primarily composed of cellulose, which is naturally prone to fibrillation in wet conditions. It is possible that splitting of cellulose fibers creates additional fiber ends for entanglement and prevents or hinders full dispersion. An example of cellulose fibres taken from undispersed portions of wipes are shown in
Figure 2. Preventing fibrillation could enable stronger (more entangled) wipes to fully disperse.
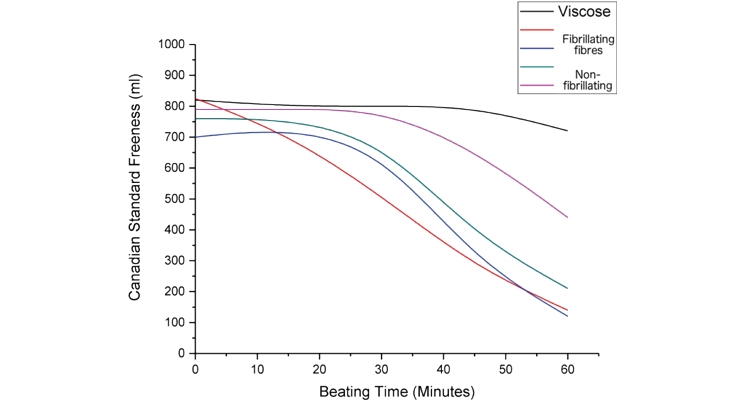
To test this hypothesis, wetlaid-hydroentangled wipes were produced from cellulose fibers with differing levels of resistance to fibrillation, which included viscose, which does not fibrillate. In order to test the level of fibrillation of the fibers they were beaten and their Canadian Standard Freeness (CSF) tested. The test is designed to test the ‘freeness’ of wood pulp, i.e. the degree of refining before papermaking, whereby the fiber is blended in an aqueous suspension before draining. The overflow during draining is measured and is reported as the CSF in ml; higher CSF is indicative of lower fibrillation. Figure 3 shows the relationship between the beating time and the CSF. Viscose and the non-fibrillating fibers were found to be more resistant to fibrillation.
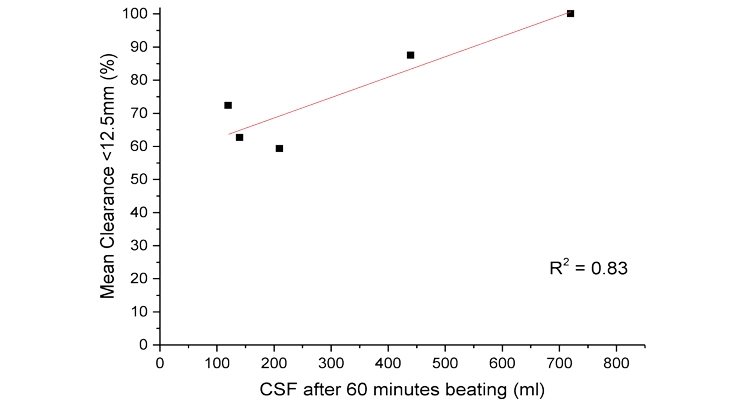
Wetlaid-hydroentangled wipes constructed from blends of wood pulp and the regenerated cellulose fibers were subjected to dispersibility testing using the INDA/EDANA shake-flask method. The proportion of wipe clearing a 12.5 mm screen was measured and plotted against CSF, shown in Figure 4.
A positive correlation was observed between fibrillation resistance and dispersibility suggesting that preventing fibrillation can be one of the options for enhancing dispersibility. This may in turn, allow greater levels of entanglement of fibers in the wipe and lead to higher wet strength.
References
1. B. Lang, Evaluation of Pre-moistened, Water-dispersible Fabrics, University of Leeds, 2010.
2. M. Tipper, Flushability of Nonwoven Wet Wipes, University of Leeds, 2015.
The fourth edition of the INDA/EDANA guidelines (GD4), published in May 2018, details a technical protocol for assessing the flushability of wipes, as well as a label code of practice. To comply with the flushability test protocols, the composition of wet wipes should be carefully considered. The fibers that make up the wipe substrate will have a direct influence on the biodegradation performance, both aerobic and anaerobic as well as the buoyancy (settling) and toilet and drain-line clearance performance.
Disintegration (dispersibility) is a key property of flushable wipes. The ability of a wipe to break up helps to:
- Prevent blockages if wipes become snagged on pipework.
- Enable wipes to pass screens that remove solids at the entry of wastewater treatment plants.
- Prevent municipal and household pump blockages.
- Reduce energy use by wastewater pumps.
Traditional routes of producing nonwoven wipes, such as carding-hydroentanglement and airlaid-chemical bonding have not proved optimal for producing dispersible substrates, which has led to wetlaid-hydroentanglement platforms being preferred. Cellulose fibers (both wood pulp and regenerated cellulose) are wet-formed and then entangled together using high-pressure water jets to mechanically entangle the fibers together and produce the dispersible wipe substrate. The energy imparted by the water jets is important in increasing the strength with higher inputted energy leading to higher strength but also reduced dispersibility. A relatively linear relationship between hydroentanglement energy, wet strength and dispersibility is shown in figure 1.
It is possible, however, to observe much higher variation in dispersibility when the wet breaking strength is above 4 N/25mm, suggesting that factors other than strength influence dispersion performance. So what are the causes of this variation in dispersibility?
Flushable wipes are primarily composed of cellulose, which is naturally prone to fibrillation in wet conditions. It is possible that splitting of cellulose fibers creates additional fiber ends for entanglement and prevents or hinders full dispersion. An example of cellulose fibres taken from undispersed portions of wipes are shown in
Figure 2. Preventing fibrillation could enable stronger (more entangled) wipes to fully disperse.
To test this hypothesis, wetlaid-hydroentangled wipes were produced from cellulose fibers with differing levels of resistance to fibrillation, which included viscose, which does not fibrillate. In order to test the level of fibrillation of the fibers they were beaten and their Canadian Standard Freeness (CSF) tested. The test is designed to test the ‘freeness’ of wood pulp, i.e. the degree of refining before papermaking, whereby the fiber is blended in an aqueous suspension before draining. The overflow during draining is measured and is reported as the CSF in ml; higher CSF is indicative of lower fibrillation. Figure 3 shows the relationship between the beating time and the CSF. Viscose and the non-fibrillating fibers were found to be more resistant to fibrillation.
Wetlaid-hydroentangled wipes constructed from blends of wood pulp and the regenerated cellulose fibers were subjected to dispersibility testing using the INDA/EDANA shake-flask method. The proportion of wipe clearing a 12.5 mm screen was measured and plotted against CSF, shown in Figure 4.
A positive correlation was observed between fibrillation resistance and dispersibility suggesting that preventing fibrillation can be one of the options for enhancing dispersibility. This may in turn, allow greater levels of entanglement of fibers in the wipe and lead to higher wet strength.
References
1. B. Lang, Evaluation of Pre-moistened, Water-dispersible Fabrics, University of Leeds, 2010.
2. M. Tipper, Flushability of Nonwoven Wet Wipes, University of Leeds, 2015.