Kin Ohmura, Contributing Editor07.15.16
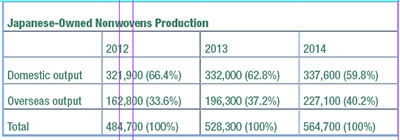
Nonwovens made outside of Japan by Japanese producers has increased from 162,800 tons in 2012 to 196,300 tons in 2013 and 227,100 tons in 2014 thanks to investments by companies including Asahi Kasei and Mitsui Chemicals. This has helped increase the overall nonwovens production by Japanese-owned companies from 484,700 tons in 2012 to 528,300 tons in 2013 and 564,700 tons in 2014.
However, investment and capacity increases within Japan have not grown as rapidly as they have outside of Japan. This has made the share of the domestic production decrease to 59.8% in 2014 from 66.4% in 2012. The percentage of domestic and overseas production was 60% and 40%, respectively in 2014.
Spunmelt technology represented the largest share of the overseas production because of this technology’s usage in the disposable baby diaper and other market areas. In 2012, spunmelt comprised 71.3% of overseas production or 116,000 tons while in 2013 it represented 71.8% or 140,800 tons and in 2014 the technology’s share 73.6% at 167,200 tons. Increases have correlated to increased use in diapers made by Japanese companies overseas.
The use of thermal bonded nonwovens in baby diapers has also increased its overseas production. The amount of this technology increased from 14,200 tons in 2012 to 28,400 tons in 2013 and 33,400 tons in 2014. The scale of production has largely increased, even though it is relatively small, compared to the spunbond or meltblown process. In terms of overseas production, the volume of spunbond and meltblown with thermal bonded nonwovens occupied 88.3% of total overseas production in 2014. This means that more than 80% of nonwovens made by Japanese manufacturers overseas serve the baby diaper market.

